Hãy vẽ cây tìm kiếm nhị phân ứng với
a) Dữ liệu tệp contacts.inp ở trong phần thực hành.
b) Từ cây nhận được ở ý a, thêm liên hệ “Anh, Nguyễn Văn Tùng, 0982 000 134”.
Hãy vẽ cây tìm kiếm nhị phân ứng với
a) Dữ liệu tệp contacts.inp ở trong phần thực hành.
b) Từ cây nhận được ở ý a, thêm liên hệ “Anh, Nguyễn Văn Tùng, 0982 000 134”.
Quảng cáo
Trả lời:
a) Dữ liệu tệp contacts.inp ở trong phần thực hành.
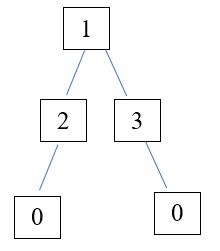
b) Từ cây nhận được ở ý a, thêm liên hệ “Anh, Nguyễn Văn Tùng, 0982 000 134”.
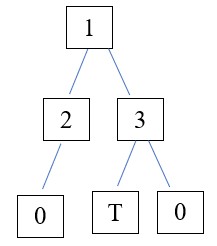
Để vẽ cây tìm kiếm nhị phân ứng với dữ liệu từ tệp contacts.inp, chúng ta cần đọc dữ liệu từ tệp và thêm các liên hệ vào cây tương ứng. Sau đó, chúng ta có thể vẽ cây đó.
Dưới đây là một phác thảo Python cho cách thực hiện điều này:
class Contact:
def __init__(self, name, phone_number):
self.name = name
self.phone_number = phone_number
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, contact):
self.contact = contact
self.left = None
self.right = None
class PhoneBook:
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def insert(self, contact):
self.root = self._insert_recursive(self.root, contact)
def _insert_recursive(self, root, contact):
if root is None:
return TreeNode(contact)
if contact.name < root.contact.name:
root.left = self._insert_recursive(root.left, contact)
elif contact.name > root.contact.name:
root.right = self._insert_recursive(root.right, contact)
return root
def display_contacts(self):
self._in_order_traversal(self.root)
def _in_order_traversal(self, root):
if root:
self._in_order_traversal(root.left)
print("Name:", root.contact.name, "- Phone:", root.contact.phone_number)
self._in_order_traversal(root.right)
# Đọc dữ liệu từ tệp contacts.inp và thêm liên hệ vào danh bạ điện thoại
phone_book = PhoneBook()
with open("contacts.inp", "r") as file:
for line in file:
parts = line.strip().split(", ")
name = parts[0]
phone_number = parts[1]
phone_book.insert(Contact(name, phone_number))
# Hiển thị toàn bộ danh sách liên hệ trước khi thêm liên hệ mới
print("Contacts before adding new contact:")
phone_book.display_contacts()
# Thêm liên hệ mới
new_contact = Contact("Anh, Nguyễn Văn Tùng", "0982 000 134")
phone_book.insert(new_contact)
# Hiển thị toàn bộ danh sách liên hệ sau khi thêm liên hệ mới
print("\nContacts after adding new contact:")
phone_book.display_contacts()
* Lưu ý thêm:
Sau khi chạy mã này, chúng ta sẽ có cây tìm kiếm nhị phân chứa tất cả các liên hệ từ tệp contacts.inp, và sau đó sẽ thêm một liên hệ mới vào cây. Tuy nhiên, để vẽ cây như bạn yêu cầu, chúng ta cần một số thư viện hỗ trợ vẽ đồ thị. Bạn có thể sử dụng thư viện như matplotlib hoặc graphviz để vẽ cây
Hot: 1000+ Đề thi giữa kì 2 file word cấu trúc mới 2026 Toán, Văn, Anh... lớp 1-12 (chỉ từ 60k). Tải ngay
CÂU HỎI HOT CÙNG CHỦ ĐỀ
Lời giải
Để thực hiện chức năng in các liên hệ ở trang n bất kỳ trong danh sách liên hệ theo thứ tự từ điển, chúng ta cần tính toán và hiển thị chỉ một phần của danh sách liên hệ tùy thuộc vào trang được yêu cầu. Dưới đây là một cách để thực hiện điều này:
class PhoneBook:
def __init__(self):
self.contacts = []
self.page_size = 20
def insert(self, contact):
self.contacts.append(contact)
self.contacts.sort(key=lambda x: x.name)
def display_contacts(self, page_number):
total_pages = (len(self.contacts) + self.page_size - 1) // self.page_size
if page_number < 1 or page_number > total_pages:
print("Invalid page number. Please enter a number between 1 and {}.".format(total_pages))
return
start_index = (page_number - 1) * self.page_size
end_index = min(start_index + self.page_size, len(self.contacts))
print("Contacts - Page", page_number, "/", total_pages)
for i in range(start_index, end_index):
print("Name:", self.contacts[i].name, "- Phone:", self.contacts[i].phone_number)
# Sử dụng
phone_book = PhoneBook()
# Thêm các liên hệ
phone_book.insert(Contact("Anh An", "0901.000.159"))
phone_book.insert(Contact("Bố", "0983 000 131"))
phone_book.insert(Contact("Mẹ", "0962 000 481"))
phone_book.insert(Contact("ICTLab Station", "024 124 000 313"))
phone_book.insert(Contact("John Doe", "123456789"))
phone_book.insert(Contact("Alice Smith", "987654321"))
phone_book.insert(Contact("Bob Johnson", "456789123"))
phone_book.insert(Contact("Anh, Nguyễn Văn Tùng", "0982 000 134"))
# Hiển thị danh sách liên hệ theo trang
page_number = int(input("Enter page number: "))
phone_book.display_contacts(page_number)
Lời giải
Để hiển thị các món trong tệp menu.inp theo thứ tự giá tiền tăng dần bằng cây tìm kiếm nhị phân, chúng ta cần đọc dữ liệu từ tệp, sau đó chèn mỗi món vào cây tìm kiếm nhị phân dựa trên giá tiền của món. Nếu có nhiều món có cùng giá tiền, chúng ta có thể sử dụng danh sách liên kết hoặc danh sách kết hợp để lưu trữ các món có cùng giá tiền. Dưới đây là một cách để thực hiện điều này:
class MenuItem:
def __init__(self, name, price):
self.name = name
self.price = price
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, menu_item):
self.menu_item = menu_item
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.same_price = [] # Danh sách các món có cùng giá tiền
class MenuDatabase:
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def insert(self, menu_item):
self.root = self._insert_recursive(self.root, menu_item)
def _insert_recursive(self, root, menu_item):
if root is None:
return TreeNode(menu_item)
if menu_item.price < root.menu_item.price:
root.left = self._insert_recursive(root.left, menu_item)
elif menu_item.price > root.menu_item.price:
root.right = self._insert_recursive(root.right, menu_item)
else:
root.same_price.append(menu_item)
return root
def display_menu_by_price(self, root):
if root:
self.display_menu_by_price(root.left)
print("Name:", root.menu_item.name, "- Price:", root.menu_item.price)
for item in root.same_price:
print("Name:", item.name, "- Price:", item.price)
self.display_menu_by_price(root.right)
# Đọc dữ liệu từ tệp menu.inp và chèn mỗi món vào cây tìm kiếm nhị phân
menu_db = MenuDatabase()
with open("menu.inp", "r") as file:
for line in file:
name, price = line.strip().split(", ")
menu_item = MenuItem(name, float(price))
menu_db.insert(menu_item)
# In danh sách món theo thứ tự giá tiền tăng dần
print("Menu sorted by price (ascending):")
menu_db.display_menu_by_price(menu_db.root)Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.