The chart below shows the results of three surveys on absenteeism in a particular European country in the years 2000, 2005 and 2010. The results show the reasons people gave for not going to work.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant. Write at least 150 words.
The chart below shows the results of three surveys on absenteeism in a particular European country in the years 2000, 2005 and 2010. The results show the reasons people gave for not going to work.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant. Write at least 150 words.
Câu hỏi trong đề: 2000 câu trắc nghiệm tổng hợp Tiếng Anh 2025 có đáp án !!
Quảng cáo
Trả lời:
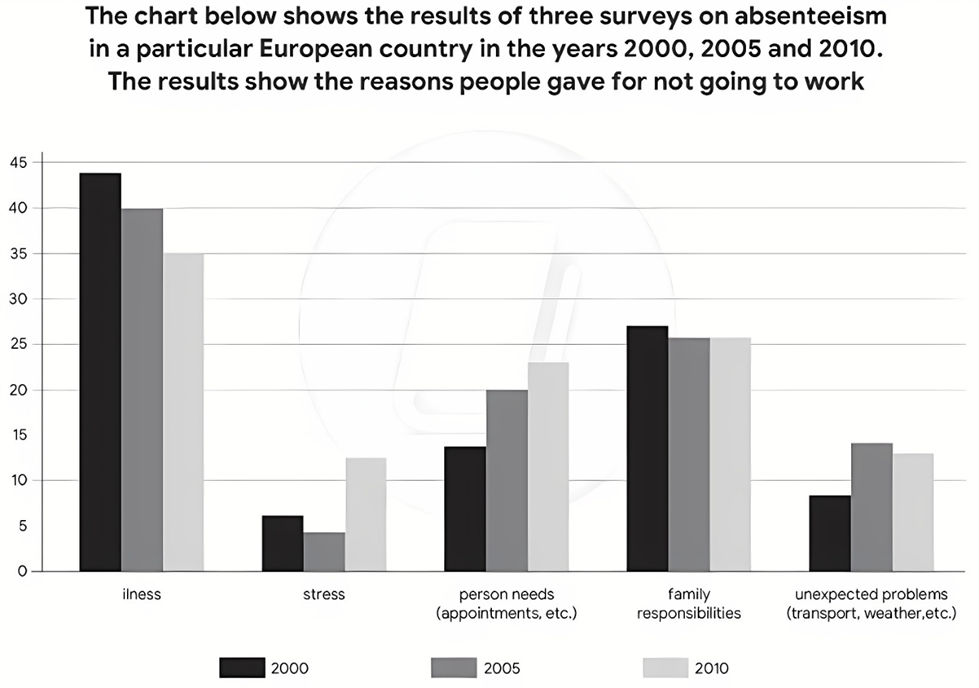
Sample 1:
The bar chart illustrates absenteeism trends in a European nation from 2000 to 2010.
In general, illness was consistently the primary reason for work absence, while stress was the least cited factor. Absenteeism due to stress, personal needs, and unforeseen issues increased, whereas cases related to illnesses and family responsibilities declined.
In 2000, a massive 45% attributed their absence to illness, which decreased steadily to 35% by 2010. Similarly, family responsibilities showed a slight dip from 27% in 2000 to just below 25% in 2005 and remained stable thereafter.
Absenteeism due to personal needs, in contrast, saw a steady rise, from roughly 13% to 23%, always ranking third. Unexpected problems causing absence exhibited a rise from 8% in 2000 to just below 15% in the commencing five years, followed by a minor drop in the five ensuing years. Conversely, stress-related absenteeism began at slightly above 5% and after a trivial drop of 3% in 2005, rebounded to around 12% by 2010.
Sample 2:
The bar chart illustrates how absenteeism rates, categorized into five different reasons, changed in a country in Europe in three separate years, namely 2000, 2005 and 2010.
Overall, while the percentages of respondents citing illness and family duties as reasons for being absent from work decreased, those citing stress, personal needs, and unexpected problems showed upward trends. Additionally, illness was consistently the major reason why people did not go to work, whereas the opposite was true in the case of stress.
In the first year, the proportion of individuals ascribing their work absence to sickness stood at nearly 45%. Despite seeing a steady decline to 35% a decade later, this reason remained the most prevalent throughout. Family obligations followed a similar trend, starting at approximately 27% before leveling off at just above 25% from 2005 to 2010.
When asked why they were not at work, initially, around 14% of people surveyed attributed it to personal needs such as appointments and so on, after which it had risen by about one-tenth by 2010. Stress, meanwhile, saw a lower growth rate, beginning at roughly 6% and ending at around 12% in the final year. An increase was also witnessed in the figure for unexpected issues (transport, weather and suchlike), growing from around 8% to peak at close to 15% after 5 years before falling minimally in 2010.
Sample 3:
The bar chart illustrates how absenteeism rates, categorized into five different reasons, changed in a European country in three distinct years: 2000, 2005, and 2010.
Overall, while the percentage of workers being absent due to illness and family obligations was on a downward trend, reasons like stress, personal needs, and unexpected problems witnessed an opposite trend. Notably, illness remains the primary reason behind work absences whereas the opposite was true in the case of stress.
In the year 2000, nearly 45% of respondents attributed their absence to sickness. Although experiencing a steady decline, reaching 35% ten years later, this reason retained its dominance. Family obligations followed a similar pattern, commencing at roughly 27% before stabilizing just above 25% between 2005 and 2010.
Approximately 14% of surveyed individuals cited personal needs, such as appointments, as the reason for missing work. This figure escalated by roughly 10% by 2010. Stress, on the other hand, displayed a more moderate growth rate, starting at around 6% and ending at nearly 12% in the final year. Unexpected issues, encompassing transportation, weather, and similar occurrences, also witnessed a rise, increasing from approximately 8% to a peak of close to 15% after five years before experiencing a slight drop in 2010.
Sample 4:
The bar chart gives information about the percentage of people who were absent from work because of five reasons in an unspecified nation in Europe over the course of 10 years from 2000 to 2010.
Overall, while there were increases in absenteeism rate due to stress, personal needs and unexpected problems, downward trends can be seen in issues related to illnesses and family responsibilities. Despite that, illness was consistently the leading factor responsible for absence from work, whereas stress remained the least stated reason, according to survey respondents.
In 2000, slightly less than 45% of surveyed individuals attributed their absence from work to illness-related issues, and despite recording a progressive drop from this point on, its figure still retained the top position, ending the period at 35%. Similar changes, but to a lesser degree, were observed in workers having to fulfill family responsibilities, whose proportion declined from approximately 27% in 2000 to almost 25% five years later, followed by another five-year period of stability until 2010.
Personal needs, such as appointments, was the only category which saw a steady growth in almost every 5-year-period, rising by nearly 10%, from roughly 13% to 23%. Meanwhile, the percentage of respondents whose unanticipated problems prevented them from going to work, which started at roughly 8% in 2000, experienced a rise to marginally under 15%, and then generally stayed at this level until the final year.
Finally, being absent from work because of suffering from stress was constantly mentioned in relatively small numbers, beginning at slightly above 5%. Although its data declined slightly, hitting a low of around 4% in 2005, it subsequently rose sharply and by 2010, had reached around 12%.
Sample 5:
The chart illustrates why workers in a European country took several days off from work in three particular years, namely 2000, 2005 and 2010.
Generally, /In general, /Overall, there was an increase in the percentages of employees being out of the office due to mental issues, personal problems and unforeseeable incidents, while the figures for physical unwellness and family duties witnessed an opposite trend. In addition, physical condition was the most common excuse for not being present at work among the reasons stated whereas mental health was the least.
About 44% of the workers surveyed being off work because of sickness in 2000, with/followed by a gradual decline to 35% in 2010. An opposite trend can be seen in the figure for those who were absent from work owing to personal requirements, which was about 14% in 2000 and grew consistently to 23% at the end of the period.
The proportion of individuals reporting family-related duties as a reason for their absence started at around 27% then dropped to 25% 5 years later and remained unchanged in the last year. Conversely, the figures for feeling stressed and unexpected adversities such as transport or weather experienced an overall growth over the period but with several fluctuations, which were approximately 6%, 4% and 13% for the former and 8%, 4% and 13% for the latter in the respective years studied.
Hot: 1000+ Đề thi giữa kì 2 file word cấu trúc mới 2026 Toán, Văn, Anh... lớp 1-12 (chỉ từ 60k). Tải ngay
CÂU HỎI HOT CÙNG CHỦ ĐỀ
Lời giải
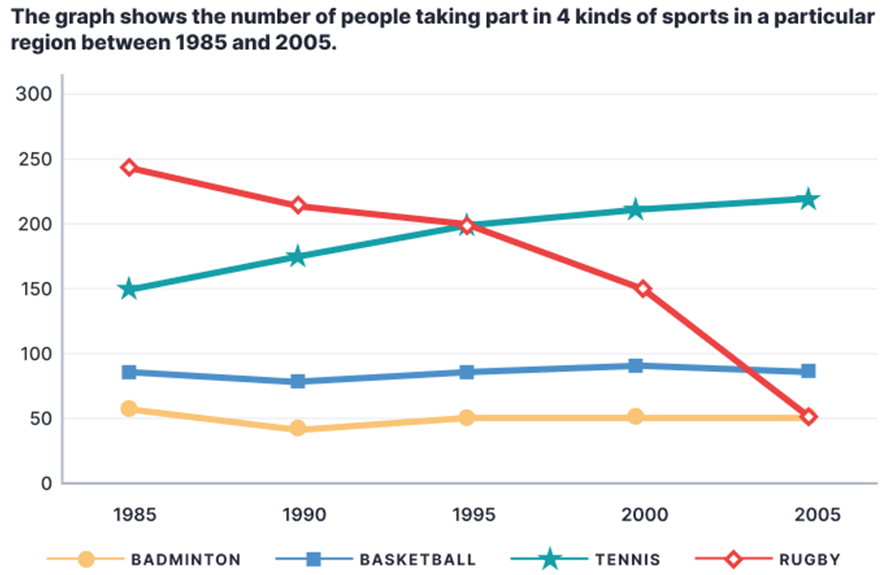
Sample 1:
The line chart illustrates how many people participated in 4 distinct types of sports in a particular area from 1985 to 2005.
Overall, rugby was the most popular sport in the first half of the period while tennis took the lead in the second half. In addition, rugby saw a downward trend while tennis took the opposite direction; moreover, the trends for basketball and badminton were relatively stable.
In 1995, the number of people playing rugby stood at just under 250, surpassing the figure for tennis players by around 100. Basketball and badminton had comparatively lower participation rates, with around 80 and 50 participants in turn.
Afterwards, the number of people participating in rugby plunged, hitting a low of 50 in 2005, equal to the figure for badminton in the same year. In contrast, the trend for tennis was upward, with its participation rate increasing to roughly 220 people at the end of the period, establishing it as the leading sport. Finally, the figures for basketball and badminton underwent negligible changes, hovering around 80 and 50 participants respectively.
Sample 2:
The line graph illustrates how many people participated in four types of sports in a specific area from 1985 to 2005. Overall, there was a significant decrease in the number of people playing rugby in this region, whereas tennis showed a gradual upward trend to become the most popular sport in the second half of the period. Additionally, throughout the period, the trends for basketball and badminton were relatively stable and comparable, with the latter sport remaining the least common.
In the first decade, rugby had the highest number of players, despite witnessing a steady fall from nearly 250 to exactly 200 participants. From 1995 onwards, this sport kept losing popularity as its figure plummeted, reaching parity with badminton (at 50 people) in the final year.
In contrast, tennis was gaining popularity and had become the dominant category by the end of the timeframe. Specifically, starting at the second highest (at 150), the number of people engaging in tennis rose continually, overtaking that of rugby in 1995 before ending at approximately 250 players.
Meanwhile, roughly 80 people played basketball initially, after which it stayed virtually unchanged until the end of the period. Badminton almost exactly mirrored this trend, albeit at a lower rate, consistently hovering around the 50 mark.
Sample 3:
The line chart compares the number of participants in basketball, tennis, badminton and rugby over a 20-year period from 1985 in a specific area.
Overall, more people played tennis throughout the period, and it was the most common sport since 1995, while rugby's popularity declined. Notably, basketball and badminton mostly had stable numbers of players.
In terms of tennis and rugby, both sports indicated inverted trends. Although rugby started at the highest point with nearly 250 players, the figure declined continually to about 200 players in 1995, when this sport was no longer the most popular. Since then, the number of people playing rugby dropped more steeply, reaching 50 in 2005. In contrast, from 1985 onwards, the figure for tennis increased steadily from second place with 150 participants. By 2005, it had reached its highest point of roughly 220 players.
In comparison, there were far fewer people who took up basketball and badminton. However, these sports remained relatively stable, with basketball having about 70 participants every year, while badminton was always the least popular with approximately 50 players each year.
Sample 4:
The line graph provides information about the number of individuals engaging in four types of sports in a specific area from 1985 to 2005.
Overall, while tennis underwent a surge in popularity, rugby experienced a decrease in participation within this region over time, with basketball and badminton remaining relatively stable. Moreover, the most drastic shift in popularity was witnessed in rugby.
At the start of the period, in 1985, rugby was the most played sport, with 240 individuals participating, and it significantly outnumbered the next sport, tennis, which had only 150 participants. Thereafter, the number of people playing rugby dropped to 200 in 1995, before plummeting to a 20-year low of 50 in the final year. This stood in stark contrast to the rise in the popularity of tennis, which saw a steady increase in participants to a peak of about 220 in 2005, making it by far the most played sport at the end of the period.
Turning to the remaining sports, in the first year, 80 individuals played basketball, almost 25 more than badminton. Over the following decade, the participant numbers for basketball rose to about 90, while those for badminton dropped to a low of 45 in 1995. In the remaining period, these two sports maintained their popularity, as the numbers participating stayed at roughly the same level until 2005.
Sample 5:
The line chart delineates the participation levels in four distinct sports in a specific area from 1985 to 2005.
Primarily, rugby emerged as the most favored sport in the initial half of the period, while tennis took precedence in the latter half. Moreover, rugby exhibited a declining trend, whereas tennis experienced a converse trajectory. Meanwhile, the engagement rates for basketball and badminton remained relatively consistent.
In 1985, the number of rugby participants stood at just below 250, exceeding the tennis players by approximately 150 individuals. Simultaneously, basketball and badminton showcased lower participation rates, with around 80 and 50 individuals involved in each sport, respectively.
Subsequently, rugby participation plummeted significantly, reaching a nadir of 50 participants in 2005, akin to the number engaged in badminton during the same year. Conversely, tennis experienced an upward trend, escalating to nearly 220 individuals by the conclusion of the period, solidifying its status as the predominant sport. In contrast, the figures for basketball and badminton remained relatively stable, with approximately 80 and 50 participants, respectively, throughout the entire duration.
Sample 6:
The given line graph delineates the participation levels in 4 different sports, namely basketball, tennis, badminton, and rugby within a specific region over a span of 20 years.
Overall, it is evident that the number of individuals participating in tennis witnessed a consistent and notable increase, contrasting sharply with the downward trend observed in rugby participation. Meanwhile, while basketball and badminton recorded lower participation rates compared to other sports, they remained relatively stable throughout the entire period.
Turning to the number of tennis players, the figures began at a relatively moderate level of 150 individuals in 1985. Subsequently, it experienced a gradual and consistent increase in participation, reaching a pinnacle of nearly 230 participants by 2005. In stark contrast, the trend of rugby involvement presented a distinctive pattern. Commencing at a relatively high level of almost 240 people, the numbers steadily declined over time and by the end of the 20-year period, rugby participants had dwindled to 50, matching the level of engagement observed in badminton. Interestingly, a point of convergence occurred in 1995, where both tennis and rugby shared a similar number of participants, with approximately 200 individuals engaging in each sport.
In regard to the remaining sports participants, the numbers for both badminton and basketball remained relatively stable over the given time frame. Beginning with approximately 50 individuals engaging in badminton and around 80 individuals involved in basketball in 1985, these figures persisted with little variation until 2005. Consequently, by the end of the period, both sports witnessed a culmination with nearly the same number of participants as they had at the beginning.
Lời giải
Sample 1:
Many young people work on a voluntary basis, and this can only be beneficial for both the individual and society as a whole. However, I do not agree that we should therefore force all teenagers to do unpaid work.
Most young people are already under enough pressure with their studies, without being given the added responsibility of working in their spare time. School is just as demanding as a full-time job, and teachers expect their students to do homework and exam revision on top of attending lessons every day. When young people do have some free time, we should encourage them to enjoy it with their friends or to spend it doing sports and other leisure activities. They have many years of work ahead of them when they finish their studies.
At the same time, I do not believe that society has anything to gain from obliging young people to do unpaid work. In fact, I would argue that it goes against the values of a free and fair society to force a group of people to do something against their will. Doing this can only lead to resentment amongst young people, who would feel that they were being used, and parents, who would not want to be told how to raise their children. Currently, nobody is forced to volunteer, and this is surely the best system.
In conclusion, teenagers may choose to work for free and help others, but in my opinion, we should not make this compulsory.
Sample 2:
Some individuals nowadays feel that youngsters should accomplish unpaid volunteer work in their leisure time for the benefit of society. I completely believe that it is critical to involve children in volunteer activity. The primary issues will be discussed with examples in this essay.
To begin with, teenagers who participate in unpaid employment are more responsible for local society. When adolescents interact with other individuals, they become aware of the issues that people face daily, such as poverty, pollution, and others. Furthermore, we have all been affected by the present COVID-19 outbreak, and many people have suffered a loss. According to "The Voice of Vietnam - VOV” a volunteer who is anti-virus and empathizes with the mental pain that the patients are experiencing, he always gives oxygen and food to those who need it the most. As a result, volunteering helps students become the most responsible citizens in the country.
Furthermore, unpaid employment can assist youngsters in broadening their social contacts and developing soft skills. Because when they work in an unpaid job, they will meet a variety of individuals and acquire a range of skills and abilities from others, such as leadership, teamwork, communication, and dealing with challenging situations. For example, a recent study in Japan discovered that students who participate in volunteer work are more sociable, enthusiastic, and tolerant of others. They will grow more extroverted, energetic, and hard-working as compared to youngsters who do not perform unpaid employment.
To conclude, I feel that rather than paying, young people should perform unpaid social work because they can acquire many important skills and are more responsible to society.
Sample 3:
There is a growing debate about whether all adolescents should be asked to perform mandatory volunteer work in their leisure time to help assist the surrounding area. Although there are a variety of benefits associated with this topic, there are also some notable drawbacks, as will now be discussed.
The advantages of teenagers doing voluntary work are self-evident. The first relevant idea is work experience. A valid illustration of this would be to increase their tangible skills. For example, an adolescent who volunteers to help in a customer service department will learn how to communicate effectively with people in different age groups. On a psychological level, the youth’s life skills will also be enhanced by having empathy towards others. This can be demonstrated by volunteering and assisting families living in low socio-economic backgrounds with their day-to-day tasks.
There are, however, also drawbacks that need to be considered. On an intellectual level, the teenager may get distracted from their study. This situation, for instance, can be seen when voluntary work is also being undertaken during school terms. There would be time constraints for both areas. On a physiological level, youth might experience fatigue as they are unaware of the acceptable working or volunteering hours and, as a result, sometimes they can be overworked.
In summary, we can see that this is clearly a complex issue as there are significant advantages and disadvantages. I personally believe that it would be better not to encourage the youths to do compulsory work because their studies might take them to a higher level in society, whereas volunteering could restrict this progress.
Sample 4:
Children are the backbone of every country. So, there are people who tend to believe that youngsters should be encouraged to initiate social work as it will result in flourished society and individualistic growth of youngsters themselves. I, too, believe that this motivation has more benefits than its drawbacks.
To begin with, social work by children can be easily associated with personality development because, during this drive, they tend to communicate with the variety of people, which leads to polished verbal skills. For example, if they start convincing rural people to send their children to school, they have to adopt a convincing attitude along with developed verbal skills to deal with the diverse kinds of people they encounter. This improved skill will help them lifelong in every arena. Apart from this, the true values of life like tolerance, patience, team spirit, and cooperation can be learned. Besides that, young minds serve the country with full enthusiasm that gives the feeling of fulfillment and self-satisfaction. This sense of worthiness boosts their self-confidence and patriotic feelings. Moreover, experiencing multiple cultures and traditions broadens their horizons and adds another feather to their cap.
However, it is truly said, no rose without thrones. Can the drawbacks of this initiation be ignored? Children go to school, participate in different curriculum activities, endure the pressure of peers, parents, and teachers and in the competitive world, they should not be expected to serve society without their self-benefits. This kind of pressure might bring resentment in their mind.
In conclusion, I believe, the notion of a teenager doing unpaid work is indeed good but proper monitoring and care should be given to avoid untoward consequences.
Sample 5:
Youngsters are the building blocks of the nation and they play an important role in serving society because at this age they are full of energy not only mentally but physically also. Some people think that the youth should do some voluntary work for society in their free time, and it would be beneficial for both of them. I agree with the statement. It has numerous benefits which will be discussed in the upcoming paragraphs.
To begin with, they could do a lot of activities and make their spare time fruitful. First of all, they can teach children to live in slum areas because they are unable to afford education in schools or colleges. As a result, they will become civilized individuals and do not indulge in antisocial activities. By doing this they could gain a lot of experience and become responsible towards society. It would be beneficial in their future perspective.
In addition to this, they learn a sense of cooperation and sharing with other people of the society. for instance, they could grow plants and trees at public places, and this would be helpful not only to make the surrounding clean and green but reduce the pollution also to great extent. Moreover, they could arrange awareness programmes in society and set an example among the natives of the state. This will make the social bonding strong between the individuals and this will also enhance their social skills.
In conclusion, they can “kill two birds with one stone” because it has a great advantage both for the society and for the adolescents. Both the parents, as well as teachers, should encourage the teens to take part in the activities of serving the community in their free time.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.