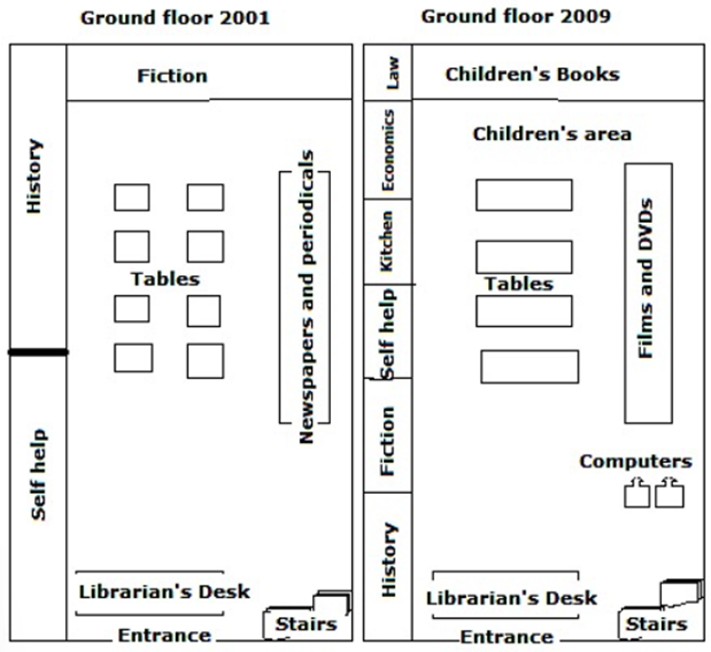
The plans below show the ground floor of a library in 2001 and how it was redeveloped in 2009.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant. Write at least 150 words.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant. Write at least 150 words.
Câu hỏi trong đề: 2000 câu trắc nghiệm tổng hợp Tiếng Anh 2025 có đáp án !!
Quảng cáo
Trả lời:
Sample 1:
The maps illustrate significant changes that occurred in the layout of a library’s ground floor between 2001 and 2009. Overall, the library underwent extensive renovations, reflecting a shift towards a more diverse collection, coupled with the inclusion of modern facilities.
In 2001, the library was organized into four main sections: Fiction at the back, History and Self Help to the left, and Newspapers & Periodicals on the right, with tables centrally located for reading and study. The librarian’s desk was situated just behind the entrance, adjacent to the stairs.
By 2009, the Fiction and History sections had been reduced in size and relocated closer to the entrance, on the left side of the librarian's desk. At the backmost part of the library, a Children’s Books area was introduced, featuring a dedicated space for children’s activities. The former History shelf is now used to accommodate Law, Economics and Kitchen books. Notably, the Newspapers & Periodicals section was completely removed and replaced with a Films & DVDs section, situated next to a newly added computer area. Throughout these changes, the original eight tables had been replaced by four longer ones.
Sample 2:
The diagrams show alterations made to the ground level of the library from 2001 to 2009.
In summary, while areas for displaying three original categories of books remained, they were relocated eight years later to accommodate various other types of books. This floor was also updated with interactive media and computer facilities.
Regarding changes in the southern section, upon entering the ground floor in 2001, readers encountered a librarian’s desk directly in front of them, with stairs on the right. Eight years later, redevelopment plans indicate no changes to these features. However, the area for self-help books on the left was moved northward and significantly reduced in size, making room for two cubicles dedicated to history and fiction books.
Regarding redevelopment in the northern part of the library, in the northwest section, previously designated for history books, visitors now had access to books in four categories: law, economics, cooking, and self-help, arranged from north to south. Another noticeable change was the transformation of the area originally for fiction books at the back of the ground floor into a section for children’s books by 2009. The central area also underwent significant changes, with eight square tables being replaced by four longer rectangular tables, and the area for newspapers and magazines converted into a space for movies and DVDs. South of this area were computers, and the open space behind the tables was turned into a children’s area.
Sample 3:
The maps illustrate the plan/layout of a ground floor of a library in 2001 and the changes introduced in it over the next eight years.
Overall, it can be seen that the library underwent four main changes. The principal change was the addition of new sections and their modernization by addition of IT facilities.
In 2001, the entrance of the library was on the south side, with the librarian's desk next to it and stairs to the upper floors to its right. The library had three sections in 2001, self-help and history along with the western wall and the fiction section along the northern wall. Besides these three sections, newspapers and periodicals were present in the east and a few square-shaped tables were there in the centre.
By 2008, the main change that was made was that the newspapers and periodicals were replaced by films and DVDs and a few computers were installed next to them. Another major change was the addition of three more sections, kitchen, economics, law along the western wall. The fiction section was also relocated along the western wall and a children's books section was made in its place. Finally, larger rectangular tables had been placed instead of the squared shaped ones and the area between the tables and children's section was demarcated as a children’s area.
Sample 4:
The map illustrates the development of the library's ground floor in 2001 and 2009.
Overall, albeit intact in size, more sections were built in the latter plan. In addition, the appearance of technology was seen in the library after 8 years.
In 2001, passing through the entrance in the south, the librarian's desk was spotted. In the southeast corner, library users could use the stairs to access more facilities. Eight square tables were provided to learners in the centre. They were surrounded by book sections including self- help, history, fiction and newspaper and periodicals.
After 8 years, the entrance, librarian's desk and stairs' locations remained unchanged. In the middle, the small tables were replaced by four long rectangular ones, which may facilitate group discussions. The west side, which used to accommodate only two book genres, was divided into six zones containing history, fiction, self-help, kitchen, economics and laws from south to north respectively. A new sort called children's books was added, next to the children's area on the northern side. The newspaper and periodicals area was removed, giving way to films and DVDs. The most significant addition to the layout in 2009 was two computers, situated between the Films and DVDs section and the stairs.
Sample 5:
The maps give information about various alterations which occured in the arrangement of a library’s ground floor between 2001 and 2009.
Overall, the library underwent vast renovations, emphasizing a shift towards a more diverse assortment, along with the addition of modern amenities.
In 2001, the books collection was categorized into four main sections: Newspapers & Periodicals to the right, History and Self Help on the opposite side, Fiction in the north of the room with tables centrally situated for reading and study purposes. Additionally, the librarian’s desk was placed in front of the entrance, right next to the stairs.
Eight years later, the Fiction and History sections had been shrinked and repositioned closer to the entrance, adjacent to the librarian's desk. Furthermore, a dedicated area for kids was introduced at the backmost part of the library, featuring books and playground for children. The former slot for history category was utilized to accommodate Kitchen, Economics and Law contents. Remarkably, the new layout completely removed the Newspaper and periodicals section to replace it with a Films & DVDs section, with a newly added computer area on its left side. Finally, there were four long tables instead of eight small ones like in the past.
Sample 6:
The provided maps depict the floor plan of a library in 2001, and the subsequent alterations made over the following eight years.
Overall, changes primarily focus on the introduction of new sections, encompassing kitchen, economics and law, and the integration of IT facilities, indicating a modernization of the library.
In 2001, the library entrance was situated on the south side, accompanied by the librarian’s desk, with stairs leading to upper floors adjacent to it. The library was divided into three sections: self-help and history along the western wall, fiction along the northern wall, and newspapers and periodicals located in the east. Additionally, square-shaped tables occupied the central area.
By 2009, notable transformations had taken place. The newspapers and periodicals section had been replaced with films and DVDs, complemented by the installation of several computers nearby. Furthermore, three new sections - kitchen, economics, and law - were incorporated along the western wall. The fiction section underwent relocation to the same western wall, while a designated children’s books section emerged in its former place. The arrangement of tables was also revised, with larger rectangular tables replacing the previous square-shaped ones. Moreover, an area delineated as the children’s area was established between the tables and the newly designated children’s section.
Sample 7:
The maps illustrate changes that were made to the ground floor of the library between the years 2001 and 2009.
Overall, even though areas for displaying three original categories of books were still retained, these underwent relocation eight years later, making room for the incorporation of various other types of books. This ground floor was also modernized with the introduction of interactive forms of media as well as computer facilities.
Regarding changes in the southern section, upon entering the ground floor in 2001, readers had access to a librarian’s desk directly facing them, and stairs on their right-hand side. Eight years later, redevelopment plans show that no changes were made to these facilities, whereas the area for displaying self-help books to the left was relocated northwards and reduced significantly in terms of size, making way for two cubicles dedicated to showing history and fiction books.
In terms of redevelopments taking place in the northern half of the library, in the northwest area, where there was once a section for the display of books specializing in history, visitors were better catered for as they benefited from being able to read books of four various types, which were law, economics, kitchen and self-help, stretching from north to south. Another noticeable change is that there used to be an area designated for fiction books at the rear of the ground floor, but it had been transformed into that for books read by children by 2009. The central part also saw major alterations, with eight square tables being replaced by four longer and rectangular tables, and a section for newspapers and periodicals being converted into that for films and DVDs, to the south of which were computers. Finally, the open space behind the tables was turned into a children’s area.
Sample 8:
The two maps illustrate how the ground floor of a library had developed between 2001 and 2009. Overall, it can be seen that while the floor's overall size had not changed, it could provide a wider selection of materials for visitors.
In 2001, four categories of texts were located on the ground floor, namely the self-help section to the southwest, the history section to the northwest, the fiction section to the north, and newspapers and magazines to the east, across from the history shelf. Meanwhile, there were eight tables around the center of the floor to provide seating for readers. To the south of the floor was the entrance and the librarian's desk. A stairway was in the southeast, providing access to the first floor.
By 2009, while the entrance, librarian's desk and staircase had experienced no change, virtually every other space had been altered. The self-help, fiction and history shelves had been scaled down and lined up along the east side together with three new selections of kitchen, economics and law texts. Four long tables had replaced the eight tables in the center of the 2001's floor plan, and a new set of tables had occupied the space where the fiction section used to be. To the east, the newspapers and periodicals section had been repurposed into a space reserved for films and DVDs. Next to that section were a few computers for visitors to access electronic reading materials.
Sample 9:
The image illustrates the layout of a library in 2001 and its alterations in 2009. Overall, the most significant changes were the diversification of materials and the introduction of digital facilities.
Regarding 2001, eight small tables were placed in the center of the library. Self help and history materials were on the left, while fiction was on the top of the sketch. The area containing newspapers and periodicals was positioned in the far right. Furthermore, accessibility to the library was by an entrance in the centre bottom and the librarian's desk was the first thing encountered upon entering the library. The stairs were located in the bottom right corner.
As of 2009, the existing tables were replaced by four new longer ones. Children' books were introduced along the top wall, replacing fiction, which was relocated to the left- hand shelves. Moreover, additional subjects were added to this section including kitchen, economics and law. The space between children's books and the tables was dedicated for minors. However, newspapers and periodicals were no longer provided, freeing up the right side for films and DVDs, along with new computers to the bottom of the area. Finally, the entrance, the librarian's desk and the stairs underwent no modifications.
Hot: 1000+ Đề thi giữa kì 2 file word cấu trúc mới 2026 Toán, Văn, Anh... lớp 1-12 (chỉ từ 60k). Tải ngay
CÂU HỎI HOT CÙNG CHỦ ĐỀ
Lời giải
Sample 1:
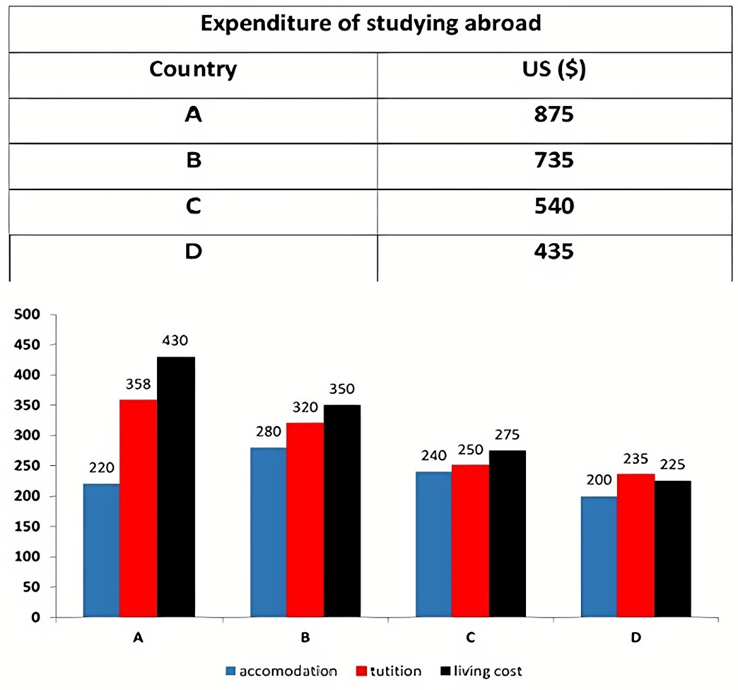
The bar graph illustrates the overseas students' spending on accommodation, tuition, and living expenses, while the table depicts information about the average weekly expenses by international students in four countries: A, B, C, and D.
Overall, foreign students need to spend the highest in country A and the lowest in D. In nearly every nation, the international students’ weekly average living expenses are the greatest, while their housing cost registers the lowest.
The costliest country for studying is A, with a weekly average expense of 875 dollars. This is followed by B, C, and D, which have weekly expenses of 735, 540, and 435 dollars, respectively. However, foreign students always pay the least for accommodation, which incurs on average weekly 220, 280, 240, and 200 dollars in the nations A, B, C, and D, respectively.
On the other hand, living expenditures account for the highest portion of average weekly costs for international students in countries A, B, and C, with 430, 350, and 275 dollars, correspondingly. Tuition fees in the same countries (A, B and C) come in second with the weekly averages of 358, 320, and 250 dollars in order. However, D is the only nation where education accounts for the highest average spending area, coming in at USD 235, followed by the cost of living (USD 225) and housing (USD 200).
Sample 2:
The table illustrates information regarding the weekly spendings by overseas students in four countries, A, B, C and D, while the bar graph depicts the students’ expenditure on the sectors, housing, education fees and living expenses.
Overall, the cost of studying abroad is the highest in country A and the lowest in D. Apart from country D, living costs account for the most part of the weekly spendings in all countries, while accommodation registers the least.
Regarding the total cost of studying, A is the most expensive country with weekly average 875 dollars, followed by B, C and D with 735, 540 and 435 dollars, respectively. On the other hand, the overseas students always spend the least on accommodation, which are on average weekly 220, 280, 240 and 200 dollars in the corresponding countries A, B, C and D.
Considering the living cost, it takes the largest share of foreign students’ average weekly expenses in countries A, B, and C with 430, 350 and 275 dollars, respectively, while tuition fees in the same countries hold the second place with weekly average 358, 320 and 250 dollars, sequentially. However, D is the only country where tuition fee occupies the highest expenditure with average weekly 235 dollars, followed by living cost (USD 225) and accommodation (USD 200.)
Sample 3:
The table and bar graph depict information regarding the weekly spendings by overseas students in countries A, B C and D.
Overall, there are three elements, housing, school fees and living costs that contribute to the total weekly spendings. The total expenditure in country A is the highest while it is the lowest in country D. Living costs account for the most part of the weekly spendings in all countries except D.
The total mean weekly cost for pupils to study in country A is US$875, next by country B at US$735, and then by country C at US$540, and finally by country D at US$435. The living costs are always the biggest component of the expenditure except for country D, with about US$10 less than the major spending which is the school fees.
Accommodation accounts for the least among all spendings in all countries. The most expensive housing is found in country B, at US$280, and the cheapest in country D at US$200. The middle range can be seen in country A at US$220 and country C at US$240, respectively. Costs of the tuition fee range between US$ 358 and US$235 in country A and D, in order.
Lời giải
Sample 1:
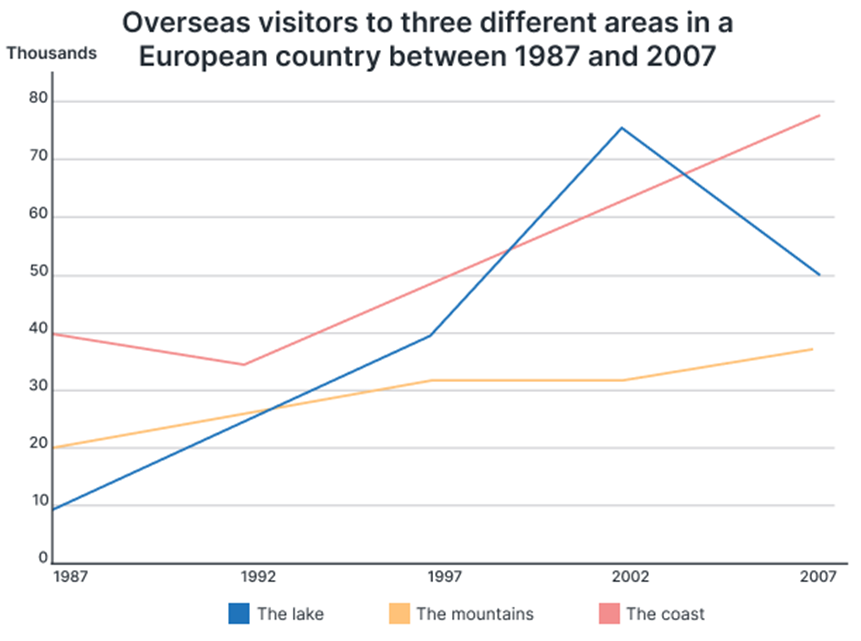
The chart illustrates a comparison of the three kinds of foreign tourist visits to a certain European nation during a twenty-year period, beginning in 1987 and ending in 2007.
Overall, the majority of survey years showed that most foreign visitors flocked to coastal locations, while mountainous places received the fewest. Furthermore, the number of visitors visiting all three locations rose throughout this time frame.
Over 40,000 tourists from outside of this European nation visited its shore in 1987. Its number plummeted to roughly 35,000 in 1992 but has steadily increased since then, peaking at over 75,000 in 2007. Meanwhile, the annual number of international visitors to the mountains ranged from 20,000 to 30,000 in the first half of the decade and then jumped to 35,000 in 2007.
For the first fifteen years, the number of international visitors to this country's lakes steadily increased, reaching a high of 75,000 in 2002. In the following years, however, this number dropped dramatically, reaching 50,000 in 2007.
Sample 2:
The chart presents a comparative analysis of three categories of foreign tourist visits to a specific European nation from 1987 to 2007.
In general, there was a consistent increase in the number of tourists across all three locations throughout the specified period. Coastal areas witnessed the highest influx of foreign tourists in almost all the periods.
The year 1987 marked the arrival of over 40,000 foreign tourists to the nation’s coastal regions. However, this figure experienced a decline, dropping to approximately 35,000 visitors by 1992. The numbers then surged significantly, peaking at over 75,000 visitors by 2007. Conversely, visits to mountainous locations started at the second highest level of 20,000, progressing to over 30,000 in 1997. Thereafter, this figure stayed unaltered towards 2002 before a modest increment to about 38,000 in 2007.
The volume of international tourists visiting the country’s lakes saw consistent growth over the initial fifteen years, reaching a pinnacle of 75,000 visitors in 2002. Subsequently, there was a substantial decline in visitation, plummeting to 50,000 by the year 2007.
Sample 3:
The graph illustrates the number of tourists to three distinct regions in a European country, spanning from 1987 to 2007. Overall, the places have experienced an increased tourist attraction from the past two decades.
Initially, the coast, with around 40,000 visitors, was known to be the most popular region among the three. On the contrary, the lakes were the least liked, only comprising around 10,000 visitors. It is also notable that both the coast and the lakes had the same number of maximum visitors in this period, which was around 75,000.
By 2007, the coast had become the most popular tourist destination, having visited by almost 75,000 visitors. Although the lakes too saw a steep rise initially, the visitors started to decline, gaining the maximum attraction of approximately 75,000 tourists in 2002. By 2007, it had declined to 40,000 visitors. The mountains surprisingly did not experience any great inclination. They only had around 15,000 more visitors since 1987.
Sample 4:
The given graph illustrates the number of overseas travellers who visited three different attractions in a European country from 1987 to 2007. It is noticeable that the number of tourists visiting all the areas witnessed an upward trend over the given period.
In 1987, the coast attracted the most overseas visitors, with 40 thousand while the converse held true for the lakes, with only 10 thousand. Over the next two decades, the number of overseas tourists opting for the lakes rose gradually to approximately 35 thousand. Similarly, there was a dramatic jump in the number of visitors to the lakes to about 75 thousand, followed by a drop to 50 thousand in 2007.
At the beginning of the period, 20 thousand tourists from other countries visited the mountains. The mentioned attractions welcomed 30 thousand visitors in 1997 and the figure remained relatively stable until 2002. At the end of the period, the number of tourists to the mountains reached the highest point of 35 thousand.
Sample 5:
The given line graph depicts information about how many foreigners visited three separate regions in a European nation, during the span of a 20-year period from 1987 to 2007.
Overall, the most notable detail is that those three regions all attracted an increasing number of foreigners. In addition, the lakes’ tourist figures witnessed the most dramatic change among those given.
In more detail, at approximately 10,000 visitors in 1987, the quantity of foreign travelers who were attracted to the lakes gradually rose to around 50,000 in 2000, before peaking at approximately 75,000 tourists in 2002, This figure then dropped back down to approximately 50,000 people in 2007.
With regards to tourist numbers in coastal and mountainous areas, the overall figures increased, however mountainous areas remained the least attractive travel option out of the three. In 1987, the number of those who chose the coast as a travel destination stood at 40,000, compared to only 20,000 travelers who went to the mountains. In the next 14 years, the coast witnessed a slight decrease in the quantity of visitors by a few thousand, which was followed by a significant climb to around 60,000 people, whereas the number of those visiting mountainous areas went up remarkably to 30,000 in 2001.
In the final 6 years, while the quantity of overseas tourists going to the coast rose moderately to above 70,000, there was a slight climb in those who paid a visit to the mountains to about 35,000.
Sample 6:
The line chart details statistics about foreign travellers to three types of tourist destinations in an unspecified nation in Europe from 1987 to 2007. Overall, all categories witnessed an upswing with the most significant growth being seen in the number of tourists to the lakeside areas.
The coastal region welcomed the highest level of alien sightseers in the first year, at 40,000. Despite dipping to about 35,000 five years later, it recovered rapidly and consistently to approximately 76,000 in the final year.
Regarding the visitors to the mountainous attractions, this figure rose moderately from 20,000 in 1987 to 30,000 in 1997. Subsequently, it documented a period of stability until 2002, followed by a rise of nearly 7,000 by the end.
Finally, starting at the lowest result of 10,000 in the beginning, the number of overseas tourists to the lakes surged to 40,000 by 1997. In the next five years, it increased more sharply to a peak of just over 75,000 which surpassed the coast, before dropping quickly back to second position with 50,000 by 2007.
Sample 7:
The given outline is the number of people who have gone to the distinctive three places (the coast, the mountains, and the lakes) in the European nation from 1987 to 2000. Looking at the by-and-large structure it is quickly clear that the number of worldwide guests to the coast has diminished over the past five years. In spite of the first moo numbers, there has been a sharp increment in the number of guests to the lake by the conclusion, whereas those going to the mountains have expanded slowly.
After dissecting the chart, it can be seen that in 1987, 40% of worldwide people went by the coast which declined to around 35% in 1992. After that, the esteem expanded to roughly 75% in 2007. While, in 1987, 20% of universal people went to see the mountains which expanded consistently to around almost 33% in 2007.
In 1987, the rate of outside guests was 10%, expanding to 40% by 1997. This figure rose to 72% in 2002, sometime recently dropping to 50% in 2007. The coast had the most elevated guest numbers among the three zones. In the interim, both the coast and the mountains experienced development in their guest tallies.
Sample 8:
The line chart outlines the number of universal sightseers gone by the diverse three places in a European nation from 1887 to 2007. The unit is measured in thousands. By and large, it can be apparent that an expansive lion's share of guests went to Europe in 2002 and 2007, and a few thousand individuals in 1987. A look at the chart reveals that more at that point 70 thousand people went by the lakes in 2002, and the same number of individuals went to the mountains in 2007. Within the same year, a decrease was observed in the number of guests who went to lakes as it was 50 thousand. In 1987, as it was, 40 thousand individuals visited the coastal regions, and after that sudden expanded drift watched from 1992 to 2007.
For the mountain ranges, 20 thousand individuals went in 1987, and exceptionally few increases were observed over a period of time. Around 35 thousand sightseers went by the mountains in 2007.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.