Một chiếc xe đang kéo căng sợi dây cáp \(AB\) trong công trường xây dựng, trên đó đã thiết lập hệ toạ độ \(Oxyz\) như hình vẽ dưới với độ dài đơn vị trên các trục tọa độ bằng \(1\;m\). Tìm được tọa độ của vectơ \(\overrightarrow {AB} = \left( {a;b;c} \right)\). Khi đó tính \(a + c\).
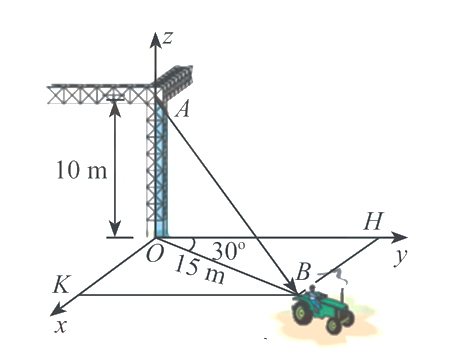
Một chiếc xe đang kéo căng sợi dây cáp \(AB\) trong công trường xây dựng, trên đó đã thiết lập hệ toạ độ \(Oxyz\) như hình vẽ dưới với độ dài đơn vị trên các trục tọa độ bằng \(1\;m\). Tìm được tọa độ của vectơ \(\overrightarrow {AB} = \left( {a;b;c} \right)\). Khi đó tính \(a + c\).

Câu hỏi trong đề: Bài tập ôn tập Toán 12 Kết nối tri thức Chương 2 có đáp án !!
Quảng cáo
Trả lời:
Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {OA} = 10\vec k \Rightarrow A\left( {0;0;10} \right)\) và \(OH = OB.\cos 30^\circ = \frac{{15\sqrt 3 }}{2}\); \(OK = OB.\cos \left( {90^\circ - 30^\circ } \right) = \frac{{15}}{2}\)
\[ \Rightarrow {\rm{ }}B\left( {\frac{{15}}{2};\frac{{15\sqrt 3 }}{2};0} \right) \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {AB} = \left( {\frac{{15}}{2};\frac{{15\sqrt 3 }}{2}; - 10} \right)\]. Vậy \(a + c = 2,5\).
Đáp án: 2,5.
Hot: 1000+ Đề thi giữa kì 2 file word cấu trúc mới 2026 Toán, Văn, Anh... lớp 1-12 (chỉ từ 60k). Tải ngay
- 20 đề thi tốt nghiệp môn Toán (có đáp án chi tiết) ( 38.500₫ )
- 500 Bài tập tổng ôn môn Toán (Form 2025) ( 38.500₫ )
- Sổ tay lớp 12 các môn Toán, Lí, Hóa, Văn, Sử, Địa, KTPL (chương trình mới) ( 36.000₫ )
- Tuyển tập 30 đề thi đánh giá năng lực Đại học Quốc gia Hà Nội, TP Hồ Chí Minh (2 cuốn) ( 150.000₫ )
CÂU HỎI HOT CÙNG CHỦ ĐỀ
Câu 1
Lời giải
Chọn B
\({\left( {3\overrightarrow a + 5\overrightarrow b } \right)^2} = 9{\overrightarrow a ^2} + 30\overrightarrow a \overrightarrow b + 25{\overrightarrow b ^2}\) \( = 9 + 90 + 25 = 124\)\( \Rightarrow \left| {3\overrightarrow a + 5\overrightarrow b } \right| = \sqrt {124} \).
Lời giải
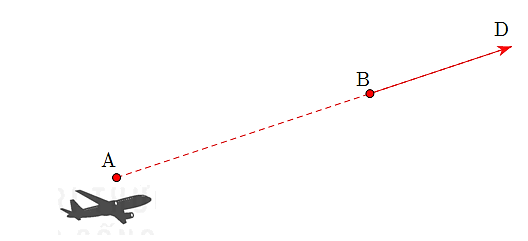
Gọi \(D\left( {x;y;z} \right)\) là vị trí của máy bay sau 10 phút bay tiếp theo (tính từ thời điểm máy bay ở điểm \(B\)). Vì hướng của máy bay không đổi nên \(\overrightarrow {AB} \) và \(\overrightarrow {BD} \) cùng hướng. Do vận tốc máy bay không đổi và thời gian bay từ \(A\) đến \(B\) bằng thời gian bay từ \[B\] đến \(D\) nên \(AB = BD\).
Do đó, \(\overrightarrow {BD} = \overrightarrow {AB} = \left( {140;50;1} \right)\).
Mặt khác: \(\overrightarrow {BD} = \left( {x - 940;y - 550;z - 8} \right)\) nên \(\left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}{x - 940 = 140}\\{y - 550 = 50}\\{z - 8 = 1}\end{array} \Leftrightarrow \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}{x = 1080}\\{y = 600}\\{z = 9}\end{array}} \right.} \right.\).
Vậy \(D\left( {1080;600;9} \right)\). Vậy tọa độ của máy bay trong 10 phút tiếp theo là \(\left( {1080;600;9} \right)\).
Suy ra \(x + y + z = 1689\).
Đáp án: 1689.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.