a) Tìm tất cả các giá trị của tham số m để phương trình \({x^2} - 2\left( {m - 1} \right)x + {m^2} - 2m - 8 = 0\) có hai nghiệm phân biệt \({x_1},\;{x_2}\) thỏa mãn \({x_1} + 6 = \sqrt {{x_2}} .\)
b) b) Cho \(f\left( x \right) = \sqrt {1 + \frac{1}{{{x^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{{\left( {x + 1} \right)}^2}}}} \) với \(x \ne 0,\;x \ne - 1\). Tính \(f\left( 1 \right) + f\left( 2 \right) + f\left( 3 \right) + \ldots + f\left( {2023} \right)\).
Quảng cáo
Trả lời:
a) Phương trình (1) có \(\Delta ' = {\left[ { - \left( {m - 1} \right)} \right]^2} - 1.\left( {{m^2} - 2m - 8} \right) = {m^2} - 2m + 1 - {m^2} + 2m + 8 = 9 > 0\;\) với mọi m \( \Rightarrow \sqrt {\Delta '} = \sqrt 9 = 3\) suy ra phương trình (1) có hai nghiệm: \(m + 2\) và \(m - 4\).
Xét hai trường hợp:
Trường hợp 1: \({x_1} = m + 2;{x_2} = m - 4\) để \({x_1} + 6 = \sqrt {{x_2}} \) thì
\(m + 2 + 6 = \sqrt {m - 4} \;\;\left( {dk:m \ge 4} \right)\)
\( \Rightarrow m + 8 = \sqrt {m - 4} \)
\( \Leftrightarrow {m^2} + 16m + 64 = m - 4\)
\( \Leftrightarrow {m^2} + 15m + 68 = 0\;\;\;\left( 2 \right)\)
Phương trình (2) có \({\Delta _m} = {15^2} - 4.1.68 = - 47 < 0\) suy ra phương trình(2) vô nghiệm
Trường hợp 2: \({x_1} = m - 4;{x_2} = m + 2\) để \({x_1} + 6 = \sqrt {{x_2}} {\rm{\;}}\)thì
\(m - 4 + 6 = \sqrt {m + 2} \;\left( {dk:m \ge - 2} \right)\)
\( \Leftrightarrow m + 2 = \sqrt {m + 2} \)
\( \Leftrightarrow \sqrt {m + 2} \left( {\sqrt {m + 2} - 1} \right) = 0\)
\( \Leftrightarrow \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{m + 2 = 0}\\{m + 2 = 1}\end{array} \Leftrightarrow \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{m = - 2}\\{m = - 1}\end{array}\;\;\left( {tm} \right)} \right.} \right.\)
Vậy \(m \in \left\{ { - 2; - 1} \right\}\)
b) Với \(a \ne 0;a \ne 1\) ta có:
\({\left( {1 + \frac{1}{a} + \frac{1}{{a + 1}}} \right)^2} = 1 + \frac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{{\left( {a + 1} \right)}^2}}} + \frac{2}{a} - \frac{2}{{a + 1}} - \frac{2}{{a\left( {a + 1} \right)}}\)
\( = 1 + \frac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{{\left( {a + 1} \right)}^2}}} + \frac{{2\left( {a + 1 - a - 1} \right)}}{{a\left( {a + 1} \right)}} = 1 + \frac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{{\left( {a + 1} \right)}^2}}}\)
\( \Rightarrow \sqrt {1 + \frac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{{\left( {a + 1} \right)}^2}}}} = 1 + \frac{1}{a} + \frac{1}{{a + 1}}\;\;\;\left( * \right)\)
Áp dụng (*) ta có:
\(f\left( 1 \right) + f\left( 2 \right) + f\left( 3 \right) + \ldots + f\left( {2023} \right)\)
=\(\sqrt {1 + \frac{1}{{{1^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{{\left( {1 + 1} \right)}^2}}}} + \;\sqrt {1 + \frac{1}{{{2^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{{\left( {2 + 1} \right)}^2}}}} + \sqrt {1 + \frac{1}{{{3^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{{\left( {3 + 1} \right)}^2}}}} + \ldots + \sqrt {1 + \frac{1}{{{{2023}^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{{\left( {2023 + 1} \right)}^2}}}} \)
= \(\sqrt {1 + \frac{1}{{{1^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{2^2}}}} + \sqrt {1 + \frac{1}{{{2^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{3^2}}}} + \sqrt {1 + \frac{1}{{{3^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{4^2}}}} + \ldots + \sqrt {1 + \frac{1}{{{{2023}^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{{2024}^2}}}} \)
= \(\left( {1 + \frac{1}{1} - \frac{1}{2}} \right) + \left( {1 + \frac{1}{2} - \frac{1}{3}} \right) + \left( {1 + \frac{1}{3} - \frac{1}{4}} \right) + \ldots + \left( {1 + \frac{1}{{2023}} - \frac{1}{{2024}}} \right)\)
= \(2024 - \frac{1}{{2024}} = \frac{{4096575}}{{2024}}\)
Hot: 1000+ Đề thi giữa kì 2 file word cấu trúc mới 2026 Toán, Văn, Anh... lớp 1-12 (chỉ từ 60k). Tải ngay
CÂU HỎI HOT CÙNG CHỦ ĐỀ
Lời giải
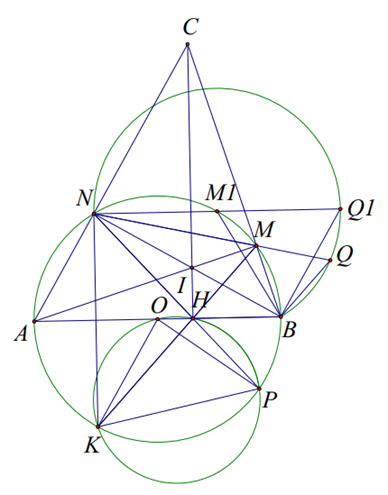
AM cắt BN tại I => I là trực tâm \(CI \bot AB\;\)
\( \Rightarrow AI \bot CB \Rightarrow B,M,C\) thẳng hàng.
Dễ thấy \(\Delta BCH \sim \Delta ICM \Rightarrow CB.CM = CI.CH\)
Dễ thấy \(\widehat {NHI} = \widehat {MHI} = \widehat {MBI} = \widehat {IAN} \Rightarrow \widehat {NHA} = \widehat {BHM}\)
Mà \(\widehat {NHA} = \widehat {KHA}\) tính chất đối xứng
\( \Rightarrow \widehat {AHK} = \widehat {BHM}\) mà \(\widehat {BHM} + \widehat {MHA} = {90^0}\)
\( \Rightarrow \widehat {AHK} + \widehat {AHM} = {180^0}\) suy ra K, H, M thẳng hàng.
b) Ta có \(\widehat {PHK} = 2.\widehat {PNK}\) (góc ngoài \(\Delta HNK\) cân)
\(\widehat {KOP} = 2\widehat {KNP}\) góc nội tiếp
\( \Rightarrow \) Tứ giác \(KOHP\) nội tiếp vì N cố định suy ra OK cố định. Vậy tâm đường tròn ngoại tiếp tam giác KHP thuộc trung trực OK.
c) Ta có \(\widehat {NMB} = {120^0}\). Trên tia đối MN lấy Q sao cho \(MB = MQ \Rightarrow \widehat {NQB} = {60^0}\)
NB cố định \( \Rightarrow Q\) thuộc cung chứa góc \({60^0}\) dựng trên NB \( \Rightarrow MN + MB\) lớn nhất khi \(NQ\) là đường kính của đường tròn
\(MB = MQ = MN \Rightarrow M \equiv M1,\;Q \equiv Q1\).
Vậy M là trung điểm cung \(NB \Rightarrow MN + MB\) lớn nhất \(MN + NB = 2R\)
Lời giải
a) Ta có: \({a^3} + {b^3} - 8{c^3} + 28{d^3} = 0 \Rightarrow {a^3} + {b^3} + {c^3} + {d^3} \vdots 3\)
\( \Rightarrow {\left( {a + b} \right)^3} - 3ab\left( {a + b} \right) + {\left( {c + d} \right)^3} - 3cd\left( {c + d} \right) \vdots 3\)
\( \Rightarrow {\left( {a + b} \right)^3} + {\left( {c + d} \right)^3} \vdots 3\)
\( \Rightarrow {\left( {a + b + c + d} \right)^3} - 3\left( {a + b} \right)\left( {c + d} \right)\left( {a + b + c + d} \right) \vdots 3\)
\( \Rightarrow {\left( {a + b + c + d} \right)^3} \vdots 3\)
\( \Rightarrow a + b + c + d \vdots 3\)
\( \Rightarrow {\left( {a + b + c + d} \right)^2} \vdots 9\) (đpcm)
b) Xét đa thức \(P\left( x \right) = a{\left( {x + 1} \right)^{1012}}{\left( {x - 2} \right)^{1012}}\), với \(a \in \mathbb{R}\), đa thức \(P\left( x \right)\) có bậc là 2024
Ta có:
\(P\left( {{x^2} - 2} \right) = a.{\left( {{x^2} - 1} \right)^{1012}}{\left( {{x^2} - 4} \right)^{1012}} = a{\left( {x + 1} \right)^{1012}}{\left( {x - 2} \right)^{1012}}{\left( {x - a} \right)^{1012}}{\left( {x + 2} \right)^{1012}}\)
\( = P\left( x \right){\left( {x - 1} \right)^{1012}}{\left( {x + 2} \right)^{1012}}\)
\( \Rightarrow P\left( {{x^2} - 2} \right)\) chia hết cho đa thức \(P\left( x \right)\)
Vậy tồn tại đa thức \(P\left( x \right) = a{\left( {x + 1} \right)^{1012}}{\left( {x - 2} \right)^{1012}}\) với hệ số thức, có bậc 2024 thỏa mãn đã thức \(P\left( {{x^2} - 2} \right)\) chia hết cho đa thức \(P\left( x \right)\).
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.