Cho biểu thức:
\[A = \left( {\frac{{\sqrt x - 2}}{{\sqrt x + 3}} + \frac{{\sqrt x - 3}}{{2 - \sqrt x }} - \frac{{9 - x}}{{x + \sqrt x - 6}}} \right):\frac{1}{{x + 2\sqrt x - 3}}\,\,\,\,\,(x \ge 0;x \ne 1;x \ne 4).\]
1. Rút gọn biểu thức A.
2. Tìm tất cả các giá trị của \(x\) để \(A > - 2\) .
Cho biểu thức:
\[A = \left( {\frac{{\sqrt x - 2}}{{\sqrt x + 3}} + \frac{{\sqrt x - 3}}{{2 - \sqrt x }} - \frac{{9 - x}}{{x + \sqrt x - 6}}} \right):\frac{1}{{x + 2\sqrt x - 3}}\,\,\,\,\,(x \ge 0;x \ne 1;x \ne 4).\]
1. Rút gọn biểu thức A.
2. Tìm tất cả các giá trị của \(x\) để \(A > - 2\) .
Quảng cáo
Trả lời:
1.\[A = \frac{{{{(\sqrt x - 2)}^2} - (\sqrt x - 3)(\sqrt x + 3) - 9 + x}}{{(\sqrt x + 3)(\sqrt x - 2)}}:\frac{1}{{\left( {\sqrt x + 3} \right)\left( {\sqrt x - 1} \right)}}\]
\[ = \frac{{{{(\sqrt x - 2)}^2} - (x - 9) - 9 + x}}{{(\sqrt x + 3)(\sqrt x - 2)}}:\frac{1}{{\left( {\sqrt x + 3} \right)\left( {\sqrt x - 1} \right)}}\]
\[ = \frac{{{{(\sqrt x - 2)}^2}}}{{(\sqrt x + 3)(\sqrt x - 2)}}:\frac{1}{{\left( {\sqrt x + 3} \right)\left( {\sqrt x - 1} \right)}}\]
\[ = \frac{{\sqrt x - 2}}{{\sqrt x + 3}}.\left( {\sqrt x + 3} \right).\left( {\sqrt x - 1} \right)\]
\[ = \left( {\sqrt x - 2} \right)\left( {\sqrt x - 1} \right) = x - 3\sqrt x + 2\]
2.\(A = x - 3\sqrt x + 2 > - 2\) \[(\forall x \ge 0;x \ne 4;x \ne 1).\]
\( \Leftrightarrow x - 3\sqrt x + 4 > 0 \Leftrightarrow {\left( {\sqrt x - \frac{3}{2}} \right)^2} + \frac{7}{4} > 0\,(\forall x \ge 0;x \ne 4;x \ne 1).\)
Vậy \(A > - 2\) với \(\forall x \ge 0;x \ne 4;x \ne 1\)
Hot: 1000+ Đề thi giữa kì 2 file word cấu trúc mới 2026 Toán, Văn, Anh... lớp 1-12 (chỉ từ 60k). Tải ngay
CÂU HỎI HOT CÙNG CHỦ ĐỀ
Lời giải
\[\frac{{{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}}}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} + \frac{{{c^2}}}{{{{(a + b - c)}^2}}} + \frac{{\sqrt {ab} }}{{a + b}} \ge 3\]\[ \Leftrightarrow \frac{{{c^2}}}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} + \frac{{{c^2}}}{{{{(a + b - c)}^2}}} + \frac{{\sqrt {ab} }}{{a + b}} \ge 2\]
Đặt \[x = \frac{a}{c}\], \[y = \frac{b}{c}\] (x, y >0)
\[{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2} + ab - 2bc - 2ca = 0\]
\[ \Leftrightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} + 1 + xy - 2x - 2y = 0 \Leftrightarrow {(x + y - 1)^2} = xy\]
Áp dụng bất đẳng thức Cô-si: \[xy \le \frac{{{{(x + y)}^2}}}{4}\]
Do đó:
\[{\left( {x + y - 1} \right)^2} \le \frac{{{{(x + y)}^2}}}{4} \Rightarrow \left[ {3\left( {x + y} \right) - 2} \right].\left[ {2 - \left( {x + y} \right)} \right] \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow \frac{2}{3} \le x + y \le 2\]
\[P = \frac{{{c^2}}}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} + \frac{{{c^2}}}{{{{(a + b - c)}^2}}} + \frac{{\sqrt {ab} }}{{a + b}}\]
\[\begin{array}{l} = \frac{1}{{{x^2} + {y^2}}} + \frac{1}{{{{(x + y - 1)}^2}}} + \frac{{\sqrt {xy} }}{{x + y}} = \frac{1}{{{x^2} + {y^2}}} + \frac{1}{{xy}} + \frac{{\sqrt {xy} }}{{x + y}}\\ = \left( {\frac{1}{{{x^2} + {y^2}}} + \frac{1}{{2xy}}} \right) + \left( {\frac{1}{{2xy}} + \frac{{\sqrt {xy} }}{{x + y}}} \right) \ge \frac{4}{{{{(x + y)}^2}}} + 2\sqrt {\frac{1}{{2(x + y)\sqrt {xy} }}} \end{array}\]
\[P \ge \frac{4}{{{2^2}}} + 2\sqrt {\frac{1}{{2.2}}} = 2\]
Dấu bằng xảy ra khi x = y =1\[ \Leftrightarrow \]a = b = c.
Lời giải
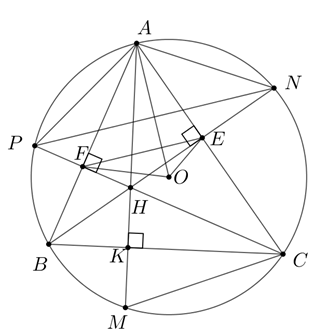
1.\(\widehat {BEC} = \widehat {BFC} = {90^0} \Rightarrow \) tứ giác \(BCEF\) nội tiếp đường tròn đường kính \(BC\)
\( \Rightarrow \widehat {CBE} = \widehat {CFE}\) ( góc nội tiếp cùng chắn cung )
Mà \(\widehat {CBE} = \widehat {CPN}\)( góc nội tiếp cùng chắn cung )
\( \Rightarrow \widehat {CFE} = \widehat {CPN} \Rightarrow EF\,//\,PN\,\)
2.\[\widehat {ABN} = \widehat {ACP}\] (cùng phụ với \(\widehat {BAC}\) )
\( \Rightarrow AN = AP\,\,\)
\(ON = OP = R\)
\( \Rightarrow A,\,O\)nằm trên đường trung trực của \(PN\)
\( \Rightarrow AO \bot PN\)
Mà \(EF\,//\,PN\, \Rightarrow AO \bot EF \Rightarrow {S_{AEOF}} = \frac{{EF.R}}{2}\)
3.\(\widehat {BAM} = \widehat {BCM}\) ( góc nội tiếp cùng chắn cung )
\(\widehat {BAM} = \widehat {BCF}\) (cùng phụ với \(\widehat {ABC}\))
\( \Rightarrow \widehat {BCF} = \widehat {BCM}\)
\(\Delta MCH\) có \(CK\) vừa là đường phân giác vừa là đường cao
\( \Rightarrow \)\(\Delta MCH\)cân tại \(C \Rightarrow K\) là trung điểm của \(MH\)
\[\begin{array}{l}\frac{{AM}}{{AK}} + \frac{{BN}}{{BE}} + \frac{{CP}}{{CF}} = \frac{{AK + KM}}{{AK}} + \frac{{BE + EN}}{{BE}} + \frac{{CF + FP}}{{CF}}\\ = 3 + \frac{{KM}}{{AK}} + \frac{{EN}}{{BE}} + \frac{{FP}}{{CF}}.\end{array}\]
\[\frac{{KM}}{{AK}} = \frac{{KH}}{{AK}} = \frac{{{S_{\Delta BHC}}}}{{{S_{\Delta ABC}}}}\]
Chứng minh tương tự: \[\frac{{EN}}{{BE}} = \frac{{{S_{\Delta AHC}}}}{{{S_{\Delta ABC}}}};\,\frac{{FP}}{{CF}} = \frac{{{S_{\Delta AHB}}}}{{{S_{\Delta ABC}}}}\]
\[\frac{{AM}}{{AK}} + \frac{{BN}}{{BE}} + \frac{{CP}}{{CF}} = 3 + \frac{{{S_{\Delta BHC}} + {S_{\Delta AHC}} + {S_{\Delta AHB}}}}{{{S_{\Delta ABC}}}} = 3 + 1 = 4.\]
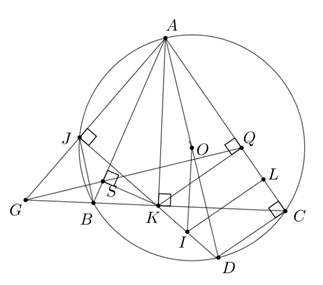
4.\[\widehat {ASK} + \widehat {AQK} = 90^\circ + 90^\circ = 180^\circ \] nên \[{\rm{AS}}KQ\] là tứ giác nội tiếp
\[ \Rightarrow \widehat {ASQ} = \widehat {AKQ}\]
\[\widehat {AKQ} = \widehat {BCQ}\] (cùng phụ với \(\widehat {CKQ}\) )
Do đó \[\widehat {ASQ} = \widehat {BCQ}\]
Suy ra \(BSQC\) là tứ giác nội tiếp.
\( \Rightarrow \widehat {GBS} = \widehat {GQC}\)
Vì \[ASKQ\]là tứ giác nội tiếp nên: \(\widehat {GQK} = \widehat {BAK}\)
Mà \(\widehat {BAK} = \widehat {GKS}\)(cùng phụ với \(\widehat {SBK}\)) nên \(\widehat {GQK} = \widehat {GKS}\)
Từ (1) và (2) \[ \Rightarrow G{K^2} = GB.GC\,\,\]
\[ \Rightarrow G{K^2} = GJ.GA \Rightarrow \frac{{GK}}{{GA}} = \frac{{GJ}}{{GK}}\]
⇒
⇒ AJ ⊥ JK
\(JK\) cắt \(\left( O \right)\) tại \(D\) (\(D\)khác \(K\)) thì \(AD\)là đường kính của \(\left( O \right)\).
Gọi \(I\) là trung điểm \(KD\), \(L\) là trung điểm \(QC\).
Khi đó \(OI\) là đường trung bình của \(\Delta AKD \Rightarrow OI{\rm{//}}AK \Rightarrow OI \bot BC\)
Mà \(OB = OC\) nên \(OI\) là trung trực \(BC\) (3)
Vì \(KQ{\rm{//}}DC\) (cùng vuông góc\(AC\)) nên \(KQCD\) là hình thang.
⇒ \(IL\) là đường trung bình của hình thang \(KQCD\)
⇒ \(IL{\rm{//}}KQ \Rightarrow IL \bot QC\)
⇒ \(IL\) là trung trực của \(QC\) (4)
Từ (3) và (4) ⇒ \(I\) là tâm đường tròn ngoại tiếp tứ giác \(BSQC\)
Vậy \(I,\,K,\,J\) thẳng hàng.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.