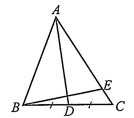
Cho nửa đường tròn đường kính \(AB\). Biết rằng \(AC\) và \(BD\) là hai dây thuộc nửa đường tròn cắt nhau tại \(E\). Tính \(\overrightarrow {AE} \cdot \overrightarrow {AC} + \overrightarrow {BE} \cdot \overrightarrow {BD} \) biết \(AB = 2\).
Cho nửa đường tròn đường kính \(AB\). Biết rằng \(AC\) và \(BD\) là hai dây thuộc nửa đường tròn cắt nhau tại \(E\). Tính \(\overrightarrow {AE} \cdot \overrightarrow {AC} + \overrightarrow {BE} \cdot \overrightarrow {BD} \) biết \(AB = 2\).
Câu hỏi trong đề: Đề kiểm tra Tích vô hướng của hai vectơ (có lời giải) !!
Quảng cáo
Trả lời:
Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {AE} \cdot \overrightarrow {AC} + \overrightarrow {BE} \cdot \overrightarrow {BD} = \overrightarrow {AE} \cdot (\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {BC} ) + \overrightarrow {BE} \cdot (\overrightarrow {BA} + \overrightarrow {AD} )\)
\( = \overrightarrow {AE} \cdot \overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AE} \cdot \overrightarrow {BC} + \overrightarrow {BE} \cdot \overrightarrow {BA} + \overrightarrow {BE} \cdot \overrightarrow {AD} {\rm{. }}\)
Vì \(AB\) là đường kính nửa đường tròn nên
Khi đó: \(\overrightarrow {AE} \cdot \overrightarrow {AC} + \overrightarrow {BE} \cdot \overrightarrow {BD} = \overrightarrow {AE} \cdot \overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {BE} \cdot \overrightarrow {BA} = \overrightarrow {AE} \cdot \overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {EB} \cdot \overrightarrow {AB} \)
\( = \overrightarrow {AB} (\overrightarrow {AE} + \overrightarrow {EB} ) = \overrightarrow {AB} \cdot \overrightarrow {AB} = {\overrightarrow {AB} ^2} = A{B^2} = 4\)
Hot: 1000+ Đề thi giữa kì 2 file word cấu trúc mới 2026 Toán, Văn, Anh... lớp 1-12 (chỉ từ 60k). Tải ngay
- Trọng tâm Lí, Hóa, Sinh 10 cho cả 3 bộ KNTT, CTST và CD VietJack - Sách 2025 ( 40.000₫ )
- Sách - Sổ tay kiến thức trọng tâm Vật lí 10 VietJack - Sách 2025 theo chương trình mới cho 2k9 ( 31.000₫ )
- Sách lớp 10 - Combo Trọng tâm Toán, Văn, Anh và Lí, Hóa, Sinh cho cả 3 bộ KNTT, CD, CTST VietJack ( 75.000₫ )
- Sách lớp 11 - Trọng tâm Toán, Lý, Hóa, Sử, Địa lớp 11 3 bộ sách KNTT, CTST, CD VietJack ( 52.000₫ )
CÂU HỎI HOT CÙNG CHỦ ĐỀ
Lời giải
|
a) Sai |
b) Đúng |
c) Sai |
d) Đúng |
a) Ta có:
b) Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {BC} = \overrightarrow {AC} - \overrightarrow {AB} ,\overrightarrow {AD} = \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {AB} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {AC} \).
Khi đó:
\(\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}{{{\overrightarrow {BC} }^2}}&{ = {{(\overrightarrow {AC} - \overrightarrow {AB} )}^2} = {{\overrightarrow {AC} }^2} - 2\overrightarrow {AC} \cdot \overrightarrow {AB} + {{\overrightarrow {AB} }^2} = {6^2} - 2 \cdot 24 + {{(4\sqrt 2 )}^2} = 20}\\{}&{ \Rightarrow BC = 2\sqrt 5 .}\\{{{\overrightarrow {AD} }^2}}&{ = {{\left( {\frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {AB} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {AC} } \right)}^2} = \frac{1}{4}\left( {{{\overrightarrow {AB} }^2} + 2\overrightarrow {AB} \cdot \overrightarrow {AC} + {{\overrightarrow {AC} }^2}} \right)}\\{}&{ = \frac{1}{4}\left[ {{{(4\sqrt 2 )}^2} + 2 \cdot 24 + {6^2}} \right] = 29 \Rightarrow AD = \sqrt {29} .}\end{array}\)
c) Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {BE} = \overrightarrow {AE} - \overrightarrow {AB} = k\overrightarrow {AC} - \overrightarrow {AB} \). Từ đó, ta có:
\(\overrightarrow {AD} \cdot \overrightarrow {BE} = \frac{1}{2}(\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AC} ) \cdot (k\overrightarrow {AC} - \overrightarrow {AB} )\)
\(\begin{array}{l} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {k\overrightarrow {AB} \cdot \overrightarrow {AC} + k{{\overrightarrow {AC} }^2} - {{\overrightarrow {AB} }^2} - \overrightarrow {AB} \cdot \overrightarrow {AC} } \right) = \frac{1}{2}\left[ {24k + {6^2} \cdot k - {{(4\sqrt 2 )}^2} - 24} \right]\\ = 30k - 28.\end{array}\)
Khi đó \(AD \bot BE \Leftrightarrow \overrightarrow {AD} \cdot \overrightarrow {BE} = 0 \Leftrightarrow 30k - 28 = 0 \Leftrightarrow k = \frac{{14}}{{15}}\).
Lời giải
|
a) Đúng |
b) Sai |
c) Sai |
d) Đúng |
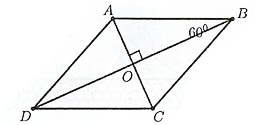
Xét hình thoi \(ABCD\) có ; tam giác \(ABC\) có đều cạnh
Ta có: ;
Ta có: ;
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.
Lời giải
Bạn cần đăng ký gói VIP ( giá chỉ từ 199K ) để làm bài, xem đáp án và lời giải chi tiết không giới hạn.